Transformative Potential of the Best Blockchain Technology

Blockchain technology, originally conceptualized as the underlying structure for Bitcoin, has evolved into a versatile and powerful tool with applications across various industries. The core idea of blockchain is a decentralized ledger of all transactions across a network, ensuring transparency, security, and immutability. This innovative technology holds the potential to revolutionize how we handle data, conduct transactions, and manage digital identities.
Understanding Blockchain Technology: The Basics
At its heart, a blockchain is a chain of blocks, where each block contains a list of transactions. Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, which means that there is no central authority or intermediary. Network participants (nodes) validate transactions through consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS).
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
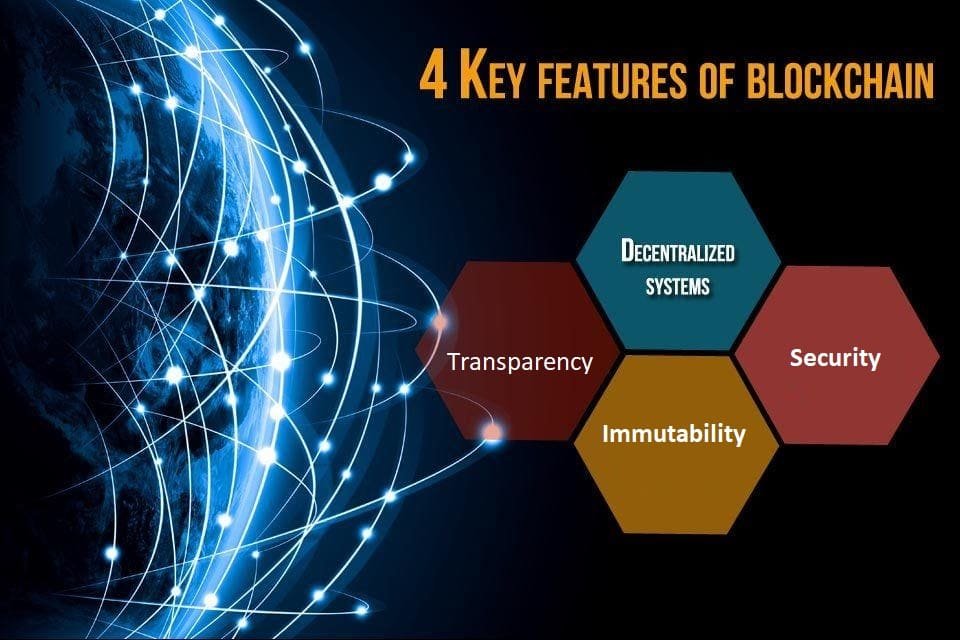
Decentralization: Unlike traditional centralized systems, blockchain operates on a distributed network, reducing the risk of single points of failure and enhancing security.
Transparency: Encouraging trust and accountability, all parties have access to the same data.
Immutability: When adding a block to the chain, its data ensures integrity by being unalterable.
Security: Blockchain uses advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data, making it highly resistant to hacking and fraud.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has applications beyond cryptocurrencies. Its unique attributes make it suitable for a wide range of applications across various sectors.
1. Financial Services
The financial industry is one of the most prominent adopters of blockchain technology. Blockchain enhances the efficiency, transparency, and security of financial transactions. Some key applications include:
Cryptocurrencies: Blockchain technology enables peer-to-peer transactions without the need for middlemen, powering digital currencies like Ethereum and Bitcoin.
Cross-Border Payments: Blockchain facilitates faster and cheaper international money transfers by eliminating the need for correspondent banks.
Smart Contracts: The terms are explicitly encoded into the code, making these contracts self-executing. When predetermined circumstances are met, they automatically enforce and carry out agreements, decreasing the need for middlemen and boosting efficiency.
2. Supply Chain Management
Blockchain can also greatly increase the efficiency and transparency of the supply chain. By providing a secure and immutable record of transactions, blockchain helps in tracking the provenance of goods, verifying authenticity, and ensuring ethical sourcing.
Traceability: Blockchain allows businesses and consumers to track products from their origin to the final destination, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Efficiency: By automating and streamlining processes, blockchain reduces delays and errors, improving overall supply chain efficiency.
Fraud Prevention: The immutable nature of blockchain records helps in preventing fraud and counterfeiting in the supply chain.
3. Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, blockchain technology can also improve data security, interoperability, and patient trust.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Blockchain enables secure sharing of patient data across different healthcare providers while maintaining privacy and data integrity.
Clinical Trials: Blockchain can also ensure the integrity of clinical trial data, making it tamper-proof and verifiable.
Drug Traceability: It helps in tracking the entire lifecycle of pharmaceutical products, ensuring their authenticity and preventing counterfeit drugs.
4. Voting Systems
Blockchain technology offers a transparent and secure solution for voting systems, potentially transforming how elections are conducted.
Transparency: Blockchain provides a public and then verifiable ledger of votes, ensuring transparency in the electoral process.
Security: By using cryptographic methods, blockchain can also prevent tampering and ensure the integrity of votes.
Accessibility: Blockchain-based voting can also enable remote and then secure voting, increasing voter participation.
5. Real Estate
The real estate industry can also benefit from blockchain technology through improved transaction processes and enhanced transparency.
Property Transactions: Blockchain can also simplify and secure property transactions by providing a transparent and immutable record of ownership.
Smart Contracts: These can also automate various real estate processes, such as rental agreements and property sales, reducing the need for intermediaries.
Land Registry: Blockchain can also provide a secure and tamper-proof record of land ownership, reducing fraud and disputes.
Challenges and Future Prospects of Blockchain

While blockchain technology offers numerous advantages, it also faces several challenges that need to be addressed for its widespread adoption.
Blockchain Technology Challenges
Scalability: Current blockchain networks often face scalability issues, limiting their ability to handle a large number of transactions quickly.
Energy Consumption: Consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work require significant computational power, leading to high energy consumption.
Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory environment for blockchain and cryptocurrencies is still evolving, creating uncertainty for businesses and investors.
Interoperability: Different blockchain platforms often lack interoperability, making it challenging to integrate various systems.
Blockchain Technology Future Prospects
Notwithstanding these difficulties, blockchain technology appears to have a bright future. Ongoing research and development are focused on addressing these issues and enhancing the capabilities of blockchain. Potential future developments include:
Scalability Solutions: Innovations like sharding, off-chain transactions, and new consensus mechanisms aim to improve the scalability of blockchain networks.
Sustainable Practices: Efforts are being made to develop more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Stake and other hybrid models.
Regulatory Clarity: As governments and regulatory bodies gain a better understanding of blockchain technology, clearer regulations are expected to emerge, fostering greater adoption.
Interoperability Standards: Initiatives to create standard protocols for blockchain interoperability will facilitate seamless integration across different platforms and industries.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology has the potential to transform various industries by providing a secure, transparent, and decentralized way of managing data and transactions. From financial services to healthcare, supply chain management, voting systems, and real estate, the applications of blockchain are vast and diverse. Despite the challenges it faces, ongoing advancements and increased adoption are likely to cement blockchain’s role as a foundational technology in the digital age.
Read more: Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) STAR





