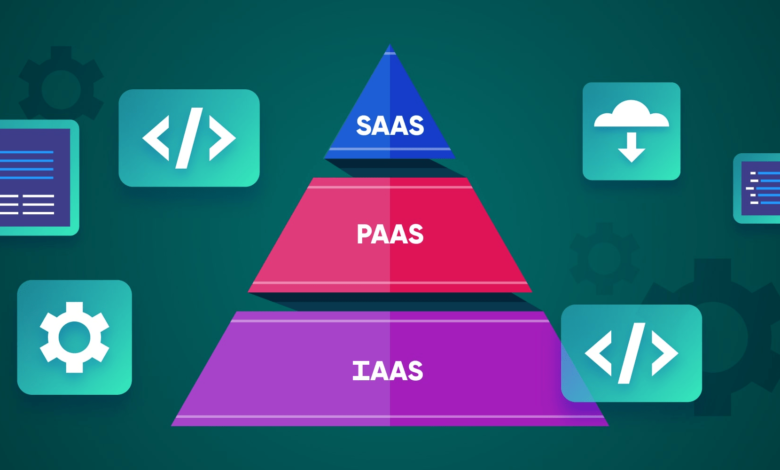
In the evolving landscape of cloud computing, understanding the differences and applications of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their operations. These three models offer distinct advantages and cater to various business needs, from infrastructure management to software deployment. This article delves into the intricacies of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS), providing a thorough analysis to help you make informed decisions.
What is IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)?

This service model is highly scalable and efficient, allowing businesses to avoid the expense and complexity of buying and managing physical servers.
Key Features of IaaS
Scalability: IaaS providers offer resources that can also be scaled up or down based on demand.
Cost-Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go pricing models reduce the need for upfront capital expenditure.
Flexibility: Users can also choose and configure the hardware and software that best meet their needs.
Automation: Many IaaS platforms offer automation tools for resource management, reducing the need for manual intervention.
Advantages of IaaS
Reduced Costs: Businesses can also save on the costs associated with purchasing and maintaining hardware.
Enhanced Performance: High-performance computing environments improve efficiency and productivity.
Business Continuity: Robust disaster recovery and backup solutions ensure data integrity and availability.
Innovative Edge: Rapid deployment of new applications and services without significant time delays.
IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS in Leading IaaS Providers
Amazon Web Services (AWS): Known for its extensive range of services and global reach.
Microsoft Azure: Offers strong integration with Microsoft products and services.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Excels in machine learning and big data analytics.
What is PaaS (Platform as a Service)?

Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure typically associated with the process.
Key Features of PaaS
Development Tools: Integrated development environments (IDEs) and other tools streamline the development process.
Middleware: software that links several services and apps together.
Database Management: Tools for creating, managing, and querying databases.
Application Hosting: Services for deploying, managing, and then scaling applications.
IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS in Advantages of PaaS
Simplified Development: Instead of worrying about infrastructure maintenance, developers can also concentrate on writing code.
Faster Time to Market: Rapidly develop and then deploy applications.
Cost Savings: Avoid the costs associated with buying and managing software licenses and then hardware.
Collaboration: Teams can also collaborate easily, as the platform is accessible from anywhere.
Leading PaaS Providers
Google App Engine: Known for its scalability and then developer-friendly tools.
Microsoft Azure: Offers a wide range of development tools and then services.
Heroku: Simplifies the deployment and then management of applications.
What is SaaS (Software as a Service)?
Software as a Service (SaaS) delivers software applications over the internet, on a subscription basis. With this strategy, businesses can also do away with the requirement to set up and execute apps on their own PCs or data centers.
Key Features of SaaS
Accessibility: Applications can also be accessed from any device with an internet connection.
Managed Services: Providers handle maintenance, updates, and then security.
Subscription-Based: Typically billed on a subscription model, reducing upfront costs.
Scalability: Services can also easily scale with user growth.
Advantages of SaaS
Cost-Effective: Reduces the need for costly hardware and then software purchases.
Ease of Use: Users can also start using the service immediately with minimal setup.
Automatic Updates: Software is regularly updated with new features and then security patches.
Accessibility: Applications can also be accessed from anywhere, facilitating remote work and collaboration.
IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS in Leading SaaS Providers
Salesforce: Known for its robust CRM capabilities.
Microsoft Office 365: Offers a suite of productivity tools accessible from anywhere.
Google Workspace: Provides a comprehensive suite of office and then collaboration tools.
Comparing IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS

Use Cases
IaaS: Ideal for businesses that require extensive control over their infrastructure, such as running custom applications or legacy software.
PaaS: Suitable for developers who need a platform to build, test, and then deploy applications quickly.
SaaS: Best for organizations looking for ready-to-use applications without the need for in-house IT management.
IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS in Cost Considerations
IaaS: Typically involves costs related to virtual machines, storage, and then networking resources.
PaaS: Pricing is usually based on the resources consumed by the applications developed and then hosted on the platform.
SaaS: Costs are usually subscription-based, often per user, per month.
IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS in Control and Flexibility
IaaS: Offers the highest level of control and then flexibility, allowing businesses to manage the entire infrastructure.
PaaS: Provides moderate control, focusing on the development and then deployment of applications.
SaaS: Offers the least control, as the provider manages everything, but it’s the most convenient and easy to use.
Conclusion
Choosing between IaaS, PaaS, and then SaaS depends on your specific business needs, technical requirements, and then budget. Each model offers unique benefits and can also significantly enhance your operational efficiency, cost management, and innovation capabilities. By understanding these differences, you can also select the most appropriate model to support your business goals and drive success in the cloud.
Read more: Electronic Engineering





