NASA Mars Human Mission: The best Leap for Mankind
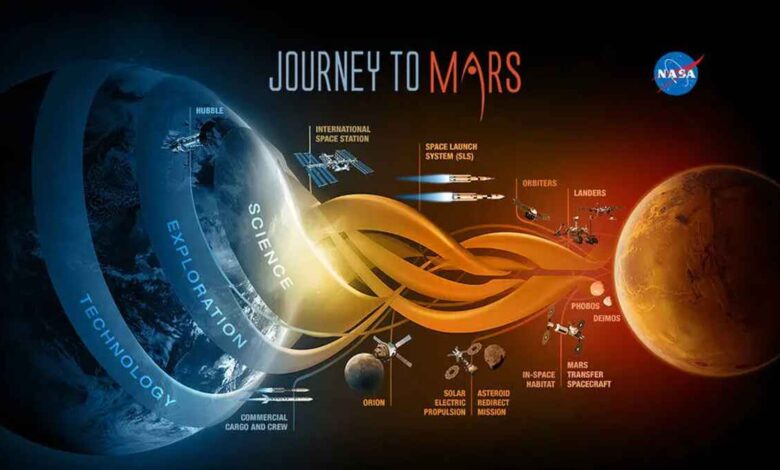
The exploration of Mars has been a long-standing dream for scientists and space enthusiasts alike. NASA’s ambitious plan to send humans to Mars is not just a leap in space exploration but a testament to human ingenuity. And the relentless pursuit of knowledge. NASA Mars human mission is poised to answer some of the most profound questions about our place in the universe. And the potential for life beyond Earth.
The Vision for Mars Exploration
Why Mars?
For millennia, people have been fascinated with Mars, also known as the Red Planet. Its proximity to Earth and the presence of water ice make it a prime candidate for exploration. Mars exploration aims to uncover the planet’s history, geology, climate, and potential for supporting life. Understanding Mars can provide insights into the past and future of our planet.
NASA’s Objectives

NASA Mars human mission has several critical objectives:
Scientific Discovery: To search for signs of past or present life on Mars.
Technological Advancement: To develop and demonstrate new technologies for future human and robotic exploration.
Human Exploration: To prepare for human missions to Mars and beyond.
Planetary Protection: To protect both Mars and Earth from cross-contamination.
Preparation and Challenges
Technological Innovations
NASA’s journey to Mars requires unprecedented technological innovations. These include:
Advanced Propulsion Systems: Faster and more efficient propulsion systems to reduce travel time.
Life Support Systems: Reliable systems to provide air, water, food, and waste management for astronauts.
Habitat Modules: Durable and safe living quarters for long-duration missions.
Extravehicular Activity (EVA) Suits: Suits designed for mobility and protection against Mars’ harsh environment.
Overcoming Challenges

The NASA Mars human mission presents numerous challenges:
Radiation Exposure: Mars lacks a magnetic field, exposing astronauts to high levels of cosmic radiation.
Psychological and Physical Health: Long-duration space travel can impact mental and physical health.
Communication Delays: The distance between Earth and Mars causes significant communication delays, complicating mission control.
Resource Utilization: Developing technologies for in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) to use Martian resources effectively.
Mission Phases
Pre-Mission Preparations
Robotic Missions: Preliminary missions like the Mars rovers and the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter have provided valuable data on Martian terrain and climate.
Simulations and Testing: Rigorous simulations and testing of equipment and procedures on Earth and the International Space Station (ISS).
Launch and Travel
Spacecraft Design: The spacecraft will be designed for a journey of approximately six to nine months.
Astronaut Selection: Highly trained astronauts will be selected for their expertise and ability to handle the rigors of space travel.
Mars Landing and Operations
Entry, Descent, and Landing (EDL): Advanced EDL techniques will ensure a safe landing on Mars.
Surface Operations: Astronauts will conduct scientific research, test new technologies, and gather samples for return to Earth.
Scientific and Social Implications

Scientific Discoveries
A human mission to Mars promises to unlock a treasure trove of scientific discoveries that could redefine our understanding of the Red Planet and, by extension, our place in the universe. The potential breakthroughs span multiple fields, each offering insights that could have profound implications for science and technology.
Geological Marvels: One of the primary objectives of a Mars mission is to conduct in-depth geological studies. By analyzing the composition, structure, and history of Mars’ surface, scientists can uncover clues about the planet’s formation and its dynamic processes over billions of years. Understanding Martian geology could also reveal the similarities and differences with Earth’s geological history, offering a comparative perspective that enhances our knowledge of planetary science.
Atmospheric Evolution: Mars’ thin atmosphere holds many secrets about the planet’s past. Studying the atmospheric composition, weather patterns, and seasonal changes will provide critical data on how Mars has evolved over time. This research could shed light on why Mars, once potentially habitable, transformed into the cold, arid world we see today. Such findings may also offer valuable lessons about Earth’s own atmospheric changes and the factors influencing climate evolution.
The Search for Life: Perhaps the most exciting prospect of a Mars mission is the search for signs of life. By exploring ancient riverbeds, underground reservoirs, and other potential habitats, scientists aim to detect biosignatures—evidence of past or present life forms. Discovering even the simplest microbial life on Mars would be a groundbreaking discovery, proving that life is not unique to Earth and raising new questions about the prevalence of life in the universe.
Social & Cultural Impact
A human mission to Mars is more than just a scientific endeavor; it holds the potential to create a lasting social and cultural impact that will resonate across generations. The mission is set to inspire, unite, and innovate, leaving an indelible mark on society and our collective future.
Inspiring the Next Generation
The Mars mission stands as a beacon of human achievement, igniting the imagination of people around the world. It has the power to motivate a new generation of engineers, explorers, and scientists to pursue careers in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics). By showcasing the possibilities of space exploration, the mission will fuel dreams and ambitions, encouraging young minds to push the boundaries of what humanity can achieve. This inspiration could lead to a surge in educational initiatives, fostering a culture of curiosity and innovation that extends far beyond the space industry.
Fostering Global Collaboration: The challenges of sending humans to Mars are immense and require the combined expertise and resources of nations across the globe. A successful mission will be a testament to the power of international collaboration, promoting unity and cooperation in a world often divided by geopolitical tensions. By working together on this monumental project, countries can build stronger diplomatic ties and lay the groundwork for future collaborative efforts in space exploration and other global challenges. This spirit of unity could help cultivate a sense of shared human identity, transcending national boundaries.
Technological Innovations with Earthly Benefits: The technological advancements required to safely transport and sustain humans on Mars will lead to a host of innovations with applications far beyond space exploration. From advancements in life support systems and renewable energy to breakthroughs in materials science and robotics, the spin-offs from the Mars mission will have a transformative impact on life here on Earth. These technologies could enhance various industries, improve sustainability, and address pressing global issues such as climate change and resource scarcity. The Mars mission, therefore, represents not just a leap for space exploration but also a catalyst for technological progress that benefits all of humanity.
The Future of Human Space Exploration
Beyond Mars
The success of NASA Mars human mission will pave the way for future human exploration of the solar system:
Lunar Missions: Establishing a sustainable presence on the Moon as a stepping stone to Mars.
Asteroid Missions: Exploring near-Earth asteroids for scientific research and resource utilization.
Deep Space Missions: Preparing for potential missions to the outer planets and beyond.
Sustainability and Long-term Goals

Sustainable space :
As humanity embarks on more ambitious journeys into space, sustainability in space exploration becomes not just a goal, but a necessity. Ensuring the long-term viability of space missions will require innovative approaches and collaborative efforts. Key to this endeavor are the development of reusable technologies, closed-loop life support systems, and the forging of international partnerships.
Reusable Technologies
The development of reusable spacecraft and habitats marks a revolutionary shift in how we approach space exploration. Traditional space missions often rely on single-use equipment, which is both costly and environmentally unsustainable. By contrast, reusable technologies promise to drastically reduce the cost of space travel, making it more accessible and frequent. These advancements include spacecraft that can withstand multiple launches and re-entries, as well as habitats that can be reconfigured and reused for different missions. This shift towards reusability is not just about efficiency—it’s about creating a sustainable foundation for continuous exploration and settlement beyond Earth.
Closed-loop Life Support: Another critical aspect of sustainable space exploration is the development of closed-loop life support systems. These systems are designed to recycle essential resources such as air, water, and food, allowing astronauts to live and work in space for extended periods without relying on constant resupply from Earth. Advances in bioregenerative technologies, which use plants and other biological processes to regenerate oxygen and purify water, are central to this effort. By creating self-sustaining ecosystems within spacecraft and habitats, we can reduce the environmental footprint of space missions and ensure that astronauts have a reliable source of life-sustaining resources, even on long-duration missions to distant planets.
International Partnerships: Achieving sustainability in space exploration requires a collaborative approach that transcends national borders. By partnering with other space agencies, private companies, and international organizations, we can pool resources, share knowledge, and distribute the risks and rewards of space missions. These partnerships are crucial for advancing technologies, standardizing practices, and addressing the complex challenges of sustainable space exploration. Moreover, international collaboration fosters peaceful relations and a shared sense of purpose, reinforcing the idea that space is a global commons that should be explored and protected for the benefit of all humankind.
Conclusion
NASA Mars human mission represents a monumental step in human history. It is not just about reaching another planet but about pushing the boundaries of what is possible, inspiring generations, and fostering global collaboration. The knowledge and technologies developed through this mission will have far-reaching implications for humanity, both on Earth and in space.
Read more: Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Healthcare

