Non-Volatile Memory: Future of the Technology

Non-volatile memory (NVM) is relied upon heavily by modern computing to permanently store and retrieve data, even when power is withdrawn. This type of memory is integral to various devices, from computers and smartphones to industrial machines and IoT devices. Unlike volatile memory, which loses its data when the power is interrupted, non-volatile memory retains data, ensuring stability and reliability in data storage.
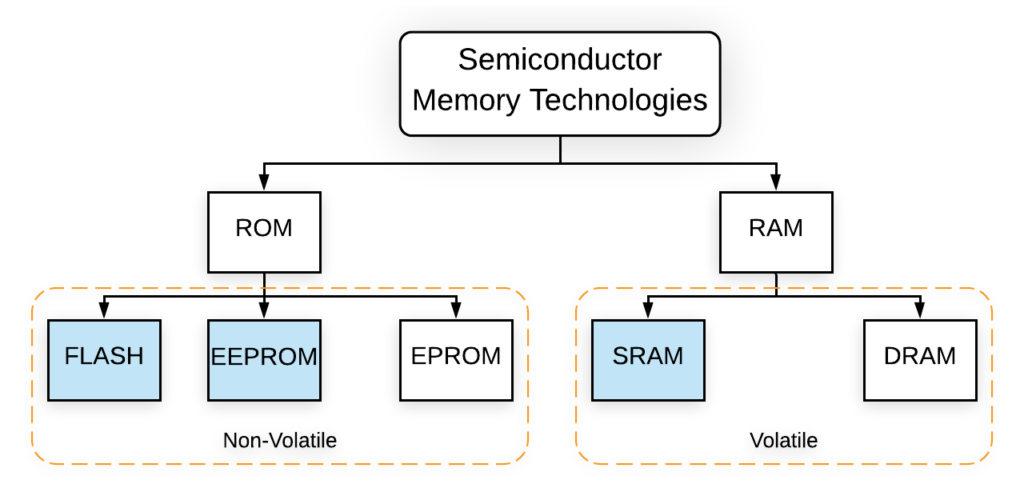
Types of Non-Volatile Memory
Non-Volatile Memory Flash Memory
Flash memory is one of the most popular forms of non-volatile memory. USB drives, SSDs (Solid State Drives), and many other portable devices use it. We appreciate flash memory for its high read/write speeds and durability. NAND and NOR flash are divided into two main types.
NAND Flash: NAND Flash, which is frequently used in SSDs and USB drives, is known for its ability to provide high-density storage and efficient write and erase cycles.
NOR Flash: Typically found in firmware storage and applications requiring fast read speeds, NOR Flash offers quick access times but lower storage density compared to NAND.
Read-Only Memory (ROM)
Read-only memory (ROM) is a classic type of non-volatile memory used primarily to store firmware, the low-level software that boots up hardware and manages its functions. There are several variations of ROM, including PROM (Programmable ROM), EPROM (Erasable Programmable ROM), and EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM).
PROM: After manufacturing, we can also program it once.
EPROM: Reprogrammable and erasable with UV light.
EEPROM: An electrically erasable and reprogrammable device allows for more versality in firmware updates by being electrically erasable and reprogrammable.
Ferroelectric RAM (FRAM)
Ferroelectric RAM (FRAM) combines the advantages of both RAM and ROM. It offers fast write speeds and high endurance with the added benefit of non-volatility. Applications using FRAM frequently log data and capture it in real-time.
Magnetoresistive RAM (MRAM)
Magnetoresistive RAM (MRAM) utilizes magnetic states to store data, providing high speed, durability, and non-volatility. Applications that demand fast data access and long-term data retention without the need for continuous power use can also utilize MRAM.
Phase-Change Memory (PCM)
Phase-change memory (PCM) operates by changing the physical state of a material between crystalline and amorphous states. PCM offers the potential for high storage density and fast read/write speeds.High-performance computing and enterprise storage solutions are explored for future use.
Applications of Non-Volatile Memory
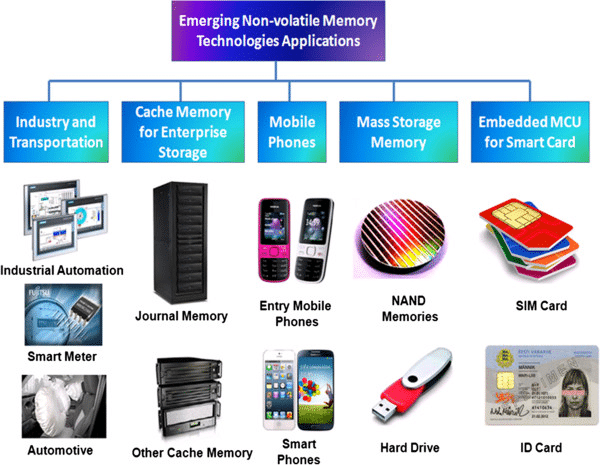
Non-volatile memory finds applications across various industries due to its reliable data retention capabilities.
Non-Volatile Memory Consumer Electronics
Consumers widely use NVM in smartphones, tablets, laptops, and cameras for consumer electronics. Flash memory in these devices stores operating systems, applications, and user data, providing quick access and reliable performance.
Non-Volatile Memory Automotive Industry
The automotive industry relies heavily on NVM for various functions, including infotainment systems, navigation, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). EEPROM and Flash memory store firmware and configuration data, ensuring safety and reliability.
Industrial Automation
In industrial automation, non-volatile memory is essential for storing configuration data, system parameters, and operational logs. It ensures that machines and control systems can also recover quickly and resume operations after power interruptions.
Healthcare Devices
Medical devices such as pacemakers, insulin pumps, and diagnostic equipment use NVM to store critical patient data and device settings. The reliability of non-volatile memory is crucial for the safe and effective functioning of these devices.
Data Centers and Enterprise Storage
Data centers and enterprise storage solutions benefit from the high speed and endurance of NVM technologies like SSDs and emerging PCM. These memory solutions offer faster data access, reduced latency, and improved energy efficiency compared to traditional hard drives.
Advantages of Non-Volatile Memory

Data Persistence
One of the primary advantages of NVM is its ability to retain data without power. This persistence is vital for applications that require reliable long-term storage and quick data recovery after power failures.
Durability and Endurance
Non-volatile memory technologies, especially SSDs and certain types of flash memory offer high endurance with a large number of read/write cycles. This durability makes them suitable for applications with intensive data usage.
Speed and Performance
Many NVM technologies, such as NAND flash and MRAM, provide high read/write speeds, enhancing the overall performance of computing devices. This speed is particularly beneficial for applications requiring quick data access and processing.
Energy Efficiency
Non-volatile memory consumes less power compared to traditional magnetic storage. This energy efficiency is important for battery-powered devices and helps reduce overall power consumption in data centers.
Challenges and Future Trends of Non-Volatile Memory

Cost Considerations
While non-volatile memory offers many advantages, the cost can be higher compared to traditional storage solutions like hard disk drives (HDDs). However, ongoing advancements and then economies of scale are gradually reducing these costs.
Scalability
As data demands grow, the scalability of NVM technologies becomes a critical factor. Researchers are continually exploring new materials and then architectures to enhance storage density and scalability.
Emerging Technologies
Emerging NVM technologies such as 3D XPoint and memristors promise to revolutionize data storage with their potential for high speed, endurance, and storage capacity. These technologies are still in development but hold significant promise for the future.
Conclusion
Non-volatile memory is a cornerstone of modern computing, offering reliable and efficient data storage across a wide range of applications. Its ability to retain data without power, coupled with high durability and performance, makes it indispensable in today’s technology landscape. As advancements continue, non-volatile memory technologies will play an even more critical role in shaping the future of data storage and management.
Read more: AI Machine Learning





